Find The #1 Foods for You: Pros & Cons Of Certain Diets
When I say ‘diet,’ you might automatically think of weight loss. However, the scope of dieting extends beyond shedding pounds; it’s about leading a healthier lifestyle. I’ll clarify the confusion surrounding various diets by discussing their core aspects and helping you identify which might align with your health goals.
Why is the word ‘personalization’ key when talking about diets? That’s because there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Because of genetics, lifestyle, and other health factors, our bodies respond to foods in unique ways. That’s why a diet that works wonders for someone else might not yield the same results for you.
With an array of diets to choose from, understanding the basic principles of each becomes essential. Some emphasize whole, unprocessed foods, while others focus on macronutrient composition like fats and carbs. Being well-informed before making significant changes to your eating habits is crucial.
So, let’s set the stage by examining a diet that harks back to our ancestors – the Paleo Diet. It’s lauded for its whole-food approach and warrants a closer look at its practicability in contemporary life. Paleo sets the stage for us to review additional diets, including Keto, DASH, Mediterranean, and plant-based options like veganism.
Contents
- 1 The Paleo Diet: A Prehistoric Eating Pattern in the Modern World
- 2 Keto Diet: High-Fat, Low-Carb Eating for Weight Loss
- 3 DASH Diet: The Heart-Healthy Plan that’s more than just Low-Sodium
- 4 The Rise of Low-Carb Diets: Benefits and Caveats
- 5 The Mediterranean Diet: A Feast of Benefits (with a Few Thorns)
- 6 Gluten-Free: Feast or Famine for Your Health
- 7 Bringing Balance to Your Plate: Choosing the Right Diet for You
The Paleo Diet: A Prehistoric Eating Pattern in the Modern World

The Paleo diet concept is simple: eat as our Paleolithic ancestors did. Proponents argue that this diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, meat, and fish, excludes grains, legumes, dairy products, and processed foods, is a genetic adaption.
One of the biggest pros of the Paleo diet is its focus on whole foods. Because the diet is naturally high in unprocessed food, there is more of an uptake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Moreover, eliminating processed foods can reduce sugar and sodium intake, which is beneficial for overall health.
However, there are cons to consider. The Paleo diet can be challenging to maintain due to its restrictive nature. It may also lead to dietary fibre and calcium deficiencies since it excludes grains and dairy. Accessibility can be another issue, as the diet often requires organic and grass-fed products, which might be cost-prohibitive for some.
Sustainability is a hot topic when it comes to the Paleo diet. Critics point out that a meat-heavy diet may not be environmentally sustainable. The carbon footprint of meat production is significant, and a proper Paleolithic diet would require meat sources that are grass-fed and free-range, making it a less viable option on a global scale.
Despite these debates, the Paleo diet has proven beneficial for some, particularly in weight management and improving symptoms of certain autoimmune diseases. As with any diet, assessing individual goals and health needs is essential before embracing this prehistoric path.
Keto Diet: High-Fat, Low-Carb Eating for Weight Loss

The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the keto diet, turns traditional macronutrient ratios on their head. By sharply cutting back on carbs and increasing fat intake, the keto diet aims to push your body into ketosis. Ketosis is where the magic – or science – happens. Your body, running low on its usual energy source, glucose, turns to burning fat for fuel.
Diving into ketosis isn’t a plunge without ripples. When you start on Keto, you may shed weight noticeably at first. The weight reduction is partly due to water loss but also because your body burns fat faster. It’s not just about dropping pounds, though; some studies suggest that a keto diet can help manage certain health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and epilepsy.
However, the high-fat chorus isn’t one without its dissonant notes. Transitioning to ketosis can present some unwelcome effects, colloquially termed the ‘keto flu,’ which include fatigue, headaches, and irritability. These symptoms are usually temporary but can be challenging hurdles for some.
Thinking long-term is crucial when considering the keto diet. High intake of saturated fats can be concerning from a cardiovascular standpoint. Getting your fats from healthy sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds is essential, as is discussing any dietary changes with a healthcare provider, especially if you have any health concerns.
DASH Diet: The Heart-Healthy Plan that’s more than just Low-Sodium

You may have heard of the DASH Diet as a go-to recommendation for managing high blood pressure. DASH, which stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, goes beyond just cutting back on salt. It emphasizes foods rich in nutrients that help lower blood pressure, such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
What sets the DASH Diet apart is its strong evidence base. Studies consistently show that following the DASH eating plan can help reduce blood pressure in a matter of weeks. Even more impressive, a lowered risk of developing cardiovascular disease over the long term is possible.
One of the most significant benefits of the DASH Diet is its focus on a balanced nutrient intake. While it encourages a higher consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins and a reduction in saturated fats, cholesterol, and trans fats, this doesn’t mean the diet is bland or restrictive. On the contrary, numerous recipes and meal ideas make it possible to enjoy a variety of tasty, heart-healthy foods.
There’s a common misconception that the DASH Diet is synonymous with uninteresting meals. However, this diet is rich in flavour. It allows for herbs and spices to enhance taste and a moderate amount of nuts, seeds, and legumes, which bring unique flavours and textures to dishes. This diet affirms that a heart-healthy eating plan does not have to compromise on taste.
To seamlessly transition into the Low-Carb Diet discussion, it’s worth noting that while the DASH Diet does not explicitly target carbohydrate reduction, it naturally limits high-sugar and high-fat foods, which typically contain lots of carbs. This ingrained approach to whole foods coincidentally aligns with some principles of low-carb eating, setting a solid foundation for our next section, where we’ll explore low-carb diets in depth.
The Rise of Low-Carb Diets: Benefits and Caveats

Low-carb diets have gained attention for their role in weight loss and blood sugar management. This approach typically involves reducing the intake of carbohydrates and increasing the consumption of protein and fats.
People often turn to low-carb diets as a strategy for shedding pounds. Some find they can control their appetite better and see quick results on the scale, providing a sense of achievement that may help with long-term diet adherence.
Besides weight control, regulating blood sugar levels is a significant advantage of this dietary approach. For those with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome, a low-carb diet can be particularly beneficial, helping to manage glucose levels and reduce reliance on medication.
However, it’s crucial to discuss potential downsides. Low-carb diets may decrease energy levels, particularly in the early phases. When the body adapts to a reduced carbohydrate intake, it can be challenging if you are highly active or involved in athletic pursuits.
The quality of fats and proteins consumed enables you to maintain long-term health. Opting for heart-healthy fats from fish, nuts, seeds, and high-quality proteins can mitigate the risk of nutritional deficiencies and other health complications.
When considering any dietary change, consulting a healthcare professional is wise, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions. Next, we move into the Mediterranean lifestyle to explore how its time-tested practices may offer different advantages for our well-being.
The Mediterranean Diet: A Feast of Benefits (with a Few Thorns)
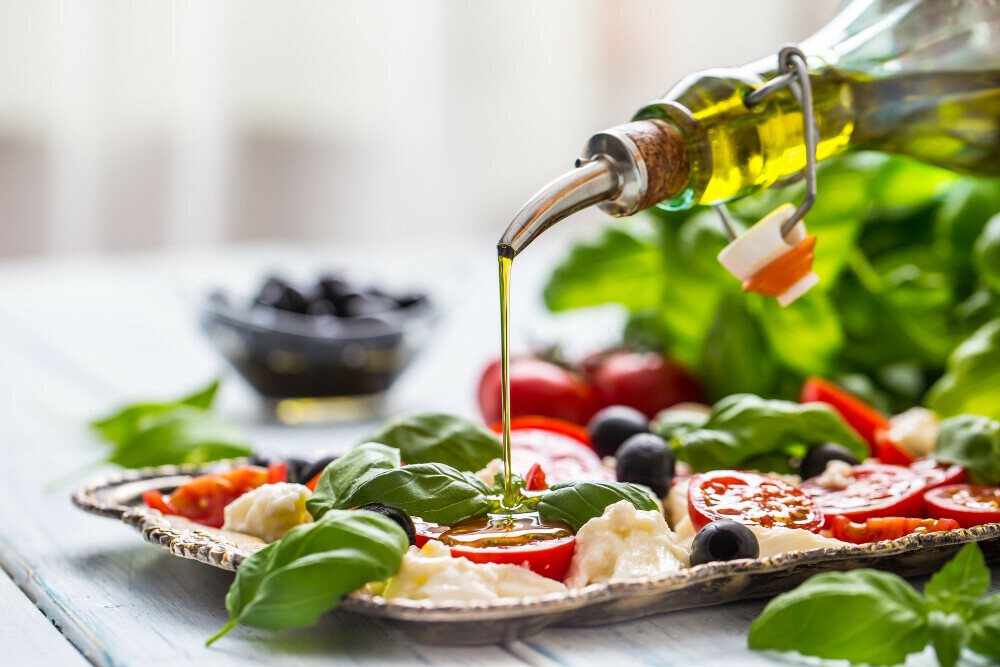

The Mediterranean diet, with its sun-kissed vegetables, olive oil drizzle, and seafood bounty, has captured hearts and minds (and maybe stomachs) around the globe. But is it all smooth sailing with this lifestyle approach to eating?
This diet boasts a plethora of health benefits. Think of reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and even Alzheimer’s. The emphasis on vegetables, legumes, and healthy fats like olive oil helps fight inflammation and keep your ticker happy. Eating Mediterranean means local, seasonal foods and minimal meat consumption, making it a win for your health and the environment. Think colourful salads, freshly caught fish, and legumes instead of factory-farmed meat. Celebrate taste!
The diet isn’t a fad with strict rules and deprivation. It’s more about embracing a way of life. Though you can still enjoy the occasional pastry or glass of wine, focus on the healthy stuff most of the time.
However, the diet requires some upfront planning and effort. Saying goodbye to processed foods and stocking up on fresh produce can seem daunting. That’s what meal-planning apps and farmers’ markets are for!
Fresh, high-quality ingredients can cost more than your typical processed fare. However, smart shopping and utilizing seasonal produce can ease the burden.
While saying no to greasy burgers or sugary treats at social gatherings can be tricky, you can always be the one bringing the delicious (and healthy) dip!
Though mostly beneficial, the Mediterranean might be challenging for some. People with certain health conditions may need to tweak the approach with their doctor’s guidance. Despite its challenges, the diet is a delicious and sustainable way to nourish your body and mind.
Gluten-Free: Feast or Famine for Your Health

Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, has become a dietary villain in recent years. But is ditching gluten a surefire path to health or a fad fraught with pitfalls? Let’s delve into the pros and cons of a gluten-free diet:
For people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, a gluten-free diet is non-negotiable. It alleviates digestive distress, bloating, and other symptoms, allowing them to thrive.
Studies suggest a gluten-free diet may lower the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers primarily due to its focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein, which are all health-promoting stars.
Gluten-free foods are lower in calories and fat, which can be helpful for weight management, especially if you choose whole, unprocessed options. Some report improved energy levels, better sleep, and more precise thinking. The benefits of adopting a gluten-free lifestyle include the elimination of inflammatory triggers or simply the psychological boost of feeling in control of your health.
However, gluten-free substitutes often lack the fibre, iron, and B vitamins in whole wheat products. Choose fortified options and incorporate other nutrient-rich foods into your diet to avoid deficiencies.
A gluten-free diet can be a life-changing boon for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. For others, it may offer some health benefits, but it comes with its own challenges. Ultimately, the decision to go gluten-free is a personal one. Weigh the pros and cons carefully, listen to your body, and consult a healthcare professional if needed. Remember, a balanced and varied diet, with or without gluten, is the key to overall health and well-being.
Bringing Balance to Your Plate: Choosing the Right Diet for You
You now have a snapshot of the diversity in diets that cater to varied health needs and ethical beliefs. From the fat-rich Keto to the produce-packed Mediterranean and the allergen-conscious Gluten-Free, there’s an approach for everyone.
The key takeaway is that personal needs and preferences should be at the forefront of any dietary decision. No one diet is the ultimate solution for everyone, and it’s crucial to consider individual health conditions, lifestyle, and nutritional needs before changing your eating habits.
Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can provide tailored advice honouring your unique circumstances. Doing so ensures that your diet supports your physical health and overall well-being.
Keep in mind that adopting any diet can require a period of adjustment. It’s normal to experience a learning curve as you explore which foods work best for you. Remember to listen to your body and be mindful of how different foods affect you physically and mentally.
Lastly, ensure you maintain a holistic approach with any diet you choose. Pair your eating habits with an active lifestyle, adequate hydration, and ample sleep to give comprehensive nourishment to your body.
To conclude, explore your options, seek expert advice, and choose a diet that aligns with YOUR life. Here’s to finding balance on your plate and joy in your meals. Remember, a diet is not just about restriction; it’s about empowerment through nourishing choices that serve your health journey.
Resources:
Gluten-Free:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/celiac-disease-diet
Low Carb
https://www.dietdoctor.com/low-carb
Keto
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ketogenic-diet-and-weight-loss
Mediterranean
DASH Diet
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000784.htm
Paleo